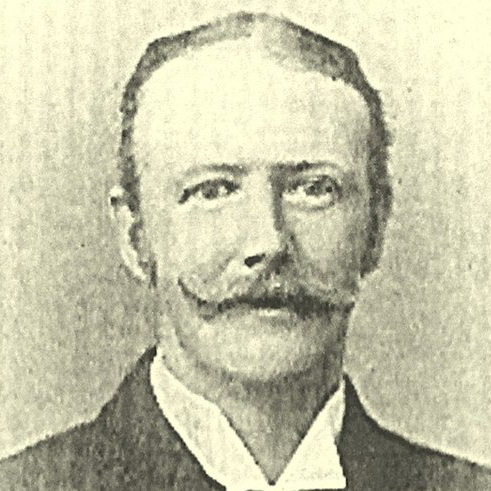
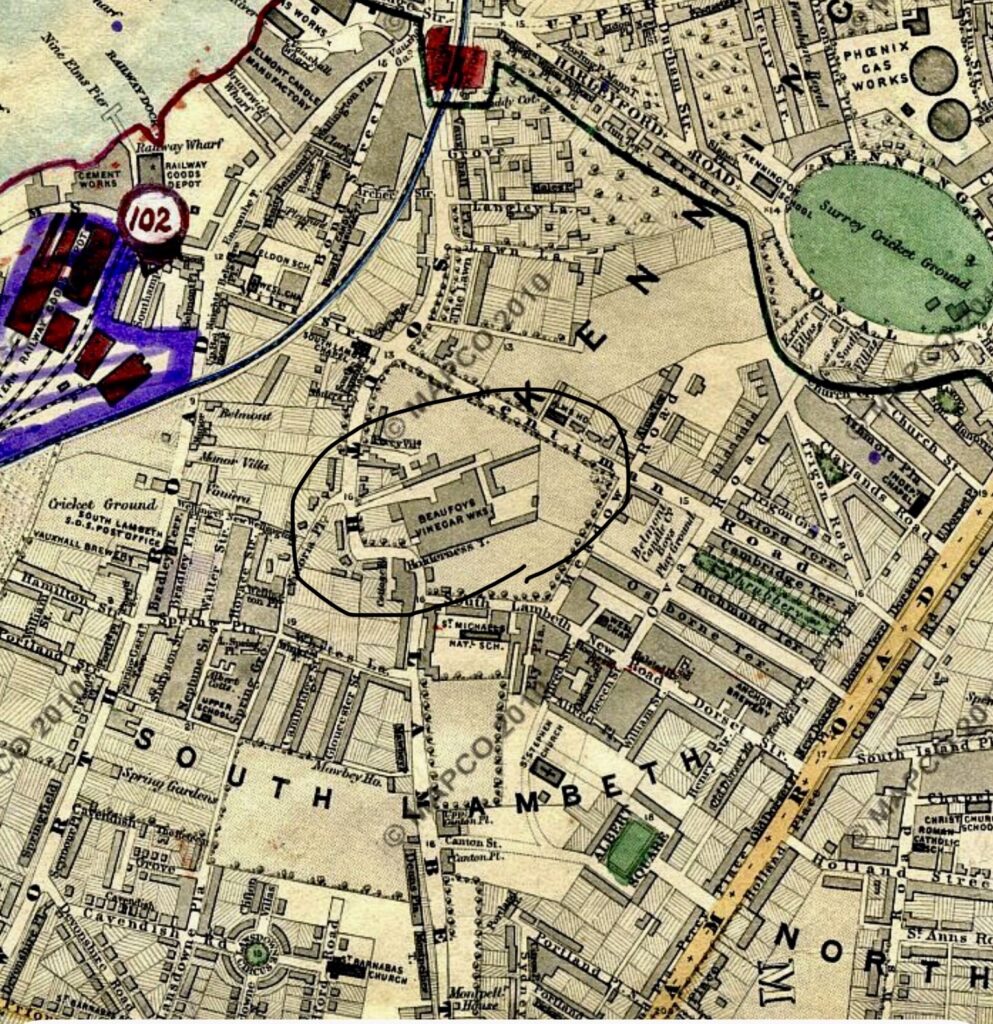
At the end of the 19th century, Vauxhall and the Thames foreshore were repositories of things and people which London needed but didn’t really want. Local man and future Kennington MP Mark Hanbury Beaufoy chose to expend his spare hours making life a bit better for the less fortunate people who lived and worked there.
In 1864 Beaufoy inherited a vinegar factory at 87 South Lambeth Road (now a handy Holiday Inn Express). Vauxhall at the time was full of poor people looking for work and at its height the factory employed 125 folks, mostly from the area. Beaufoy was a supporter of the nationwide campaign to establish an eight hour work day and implemented this in his factory to set an example to the rest of Britain.


Beaufoy’s family endowed and built the Ragged School in Newport St, Vauxhall, to provide education to destitute children who couldn’t access mainstream education. We wrote about the place in 2021. It closed after only a few decades, and Beaufoy made the decision to replace it with a vocational training school for underprivileged boys. The Beaufoy Institute then opened in Black Prince Road and this delightful, Doulton tiled building lives on as the London Diamond Way Buddhist Centre. The reason the building hasn’t turned into overpriced flats is that in his will Beaufoy stipulated that the building not be used for commercial purposes. And as if being a vinegar magnate, social reformer, and advocate of gun safety wasn’t enough, Beaufoy was also a Liberal MP for Kennington between 1889 and 1895.
If you’re a map nerd you might have noticed a preponderance of vinegar factories around Victorian London, and this is not because people had a mad passion for chippies. Instead, before refrigeration it was used as preservative for perishable foods. If you are a map nerd you might have also noticed the volume of very smelly factories (including one making, lord help us ‘essence of beef’) which dominated Vauxhall for many years. s.