From the archives, the third edition of our month of best history posts
If you’re a new arrival in the area or your interests are not so much focussed on local history, you might not be aware that for almost two centuries London’s most acclaimed pleasure garden existed on our anointed patch. Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens has been celebrated in books and songs, and even featured at key moments of the recent Netflix hit ‘Bridgerton’. While we can’t do the legendary place justice in the space of a solitary blog, we can crystallise it’s meaning by the man at the helm of its glory days in the first half of the 18th century, and his name was Jonathan Tyers (1702-1767)
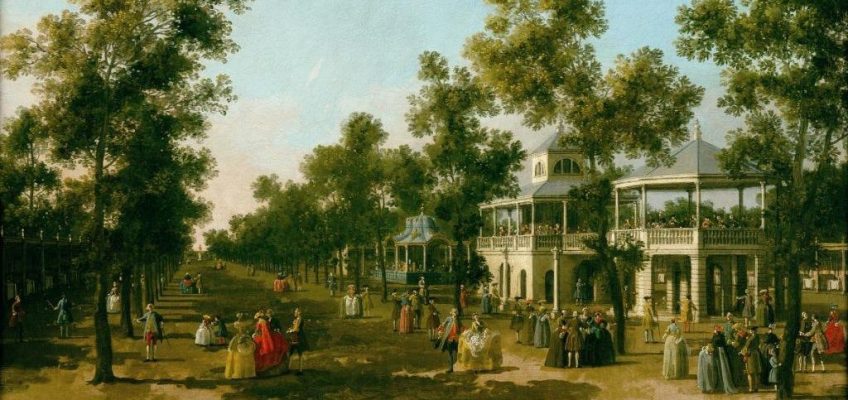

A young Jonathan Tyers subletted ‘Vauxhall Spring-Gardens’ in 1729 and undertook the hefty task of reimagining the slightly disreputable old gardens into an innocent and elegant venue for families and people of all classes. However, with an admission charge of one shilling in reality it was out of reach for most people. He was inspired by a meeting with artist and buzzkill moralist William Hogarth, who advocated the value of creating something that sent a moral message cloaked in the guise of humour and entertainment. We now refer to this as ‘family friendly’.
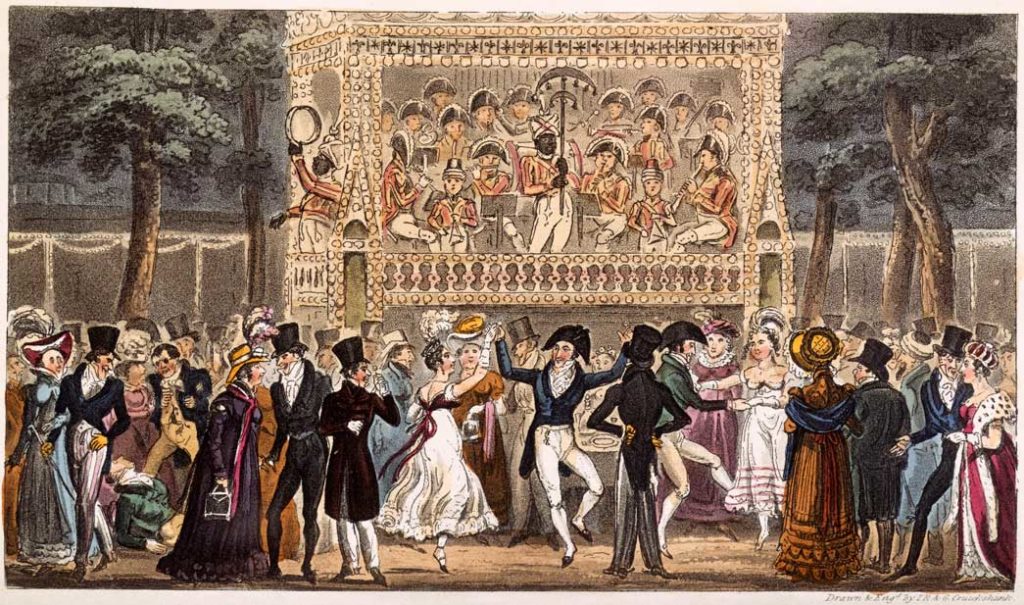

The egalitarian and polite nature of Spring Gardens was a welcome and needed riposte to a London that was violent, smelly and uncouth and it would kick start the civilisation of Georgian London. However noble, the Spring Garden regulars were still out for a bit of bawdy fun and didn’t take kindly to being preached to. Tyers had to think on his feet before the whole thing went belly up, and his masterstroke was that beyond the elegant supper boxes and promenading avenues he created a wooded and dark area called the Grove. We will leave it up your imagination what went on in the Grove, but let’s just say it was dark and proved very popular.
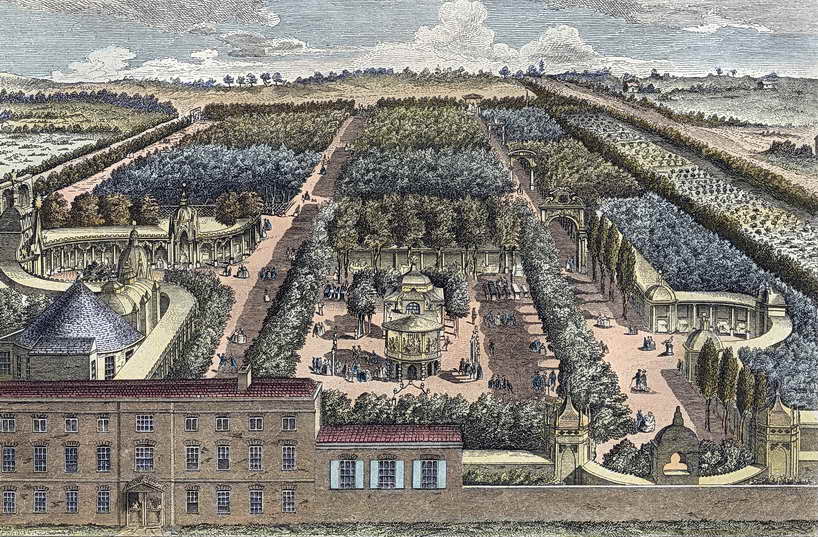
Assignations aside, what Tyers created for those who could afford it was a site for music, dancing, eating and drinking. The paintings in the supper boxes made it in reality the first public art gallery in Britain. On a typical night revellers could be entertained by performers, bands, fireworks, operas and masquerades. George Fredrick Handel became a kind of ‘artist in residence’ at the Garden and performed there regularly. When Tyers made profits he drove them directly into new structures and events, making the spot a ‘must see’ on a regular basis. After Tyers’ death in 1767 the Gardens were passed to his son and this initiated the very slow but inexorable decline of the place.
The precise location of Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens only roughly matches the footprint of the current Pleasure Gardens (created in the late 1970’s), and it’s epicentre was at the current St. Peter’s Church. Rumours of redemption from carnal sin abound about the decision to place a church on this site, and we invite you to make your own conclusion. Tyers Street is a commemoration of his efforts, both lurid and noble.
And as you can see, dear readers, attempts to gentrify Vauxhall from a place of dissolute debauchery into something more agreeable to a wealthier public for profit making purposes is by no means a contemporary undertaking.

